Real estate is the most powerful way to build wealth, and more people have become millionaires through real estate than by any other means. Despite the obvious need to save for retirement, many Americans still face financial difficulties at retirement!
Of course, you have several options for your retirement and other savings, but most of these options pale in comparison to real estate. Consider options like savings accounts, CDs, bonds, and money market accounts. These are safe options, but you certainly won’t reach a goal of building significant wealth through these means.
For the most part, these options will barely outpace inflation. Think of it. How many millionaires do you know who have become wealthy by investing in savings accounts? The stock market can bring you some interesting returns, but it can also lead to some big losses. You have very little control over the companies you invest in, and there aren’t significant tax advantages to owning stock.
Also, traditional retirement planning often falls short. Safe options like savings accounts offer minimal returns, barely keeping pace with inflation. The stock market, while potentially rewarding, is inherently risky and offers limited tax advantages.
Real estate, however, presents a powerful alternative. Historically, property values have shown a steady upward trend, unlike the stock market's unpredictable nature. Consider this: many people credit their home as their smartest investment.
The true strength of real estate lies in leverage. With a relatively small down payment, you can own a property worth considerably more, profiting from the full appreciation of its value.
Historically, real estate has provided investors with a stronger return than other options. Consider the growth of the median price of a home from 1950 to 2007 (57 years):
While there may have been a few small dips at certain points in time, the fact remains that real estate has had a strong history of steady appreciation.
Here’s an interesting experiment. If you were to ask your parents what the best investment they ever made was, what would they say? More likely than not, they’ll mention their home, and if they could do it all over again, I bet they wish they would have bought a few more.
Let’s take a simple example. Let’s say you purchase a $125,000 home today with an investment of about $15,000. If you rent this home and simply break even, you will have an asset that grows while someone else makes your mortgage, tax, and insurance payments. At a conservative 4% appreciation per year, in 30 years that home will be worth $405,000, free and clear! Not a bad return for a $15,000 investment! Think of the ways you could spend that money in retirement by simply sacrificing $15,000 today. That’s called leverage and is a major strength of investing with real estate. With the use of leverage, you can own something worth 10 times your initial investment, and still be able to take advantage of 100% of the appreciation on that asset!
Now, you may be saying to yourself, “that’s great, but I can’t wait 30 years to retire”. Real estate loans have a solution for that as well. The following chart provides some examples:
Loan scenario # 4 above shows a standard 30 year mortgage that is paid off in 30 years. However, if you were to make an additional $1,000 payment per year (loan scenario #3), that same loan would be paid off in 22.5 years! An extra $2,500 per year (scenario #2) pays it off in just 17 years. And finally, an extra $5,000 per year (scenario #1) pays it off in only 12.3 years.
By investing in carefully selected growth markets you will build your wealth and become financially independent. What are you waiting for? The best time to invest in real estate is now.
Concerned about the long-term commitment? Strategic mortgage payments can significantly shorten the loan term. This allows you to enjoy the benefits of your investment much sooner.
By targeting the right real estate markets, you can build wealth and achieve financial independence. Take action today. Real estate empowers you to take control of your financial future and secure your long-term goals.

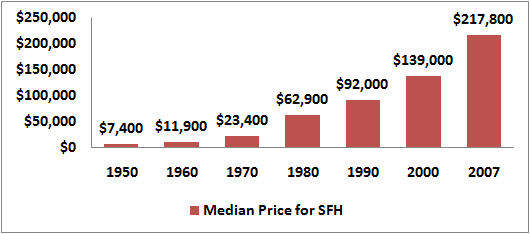
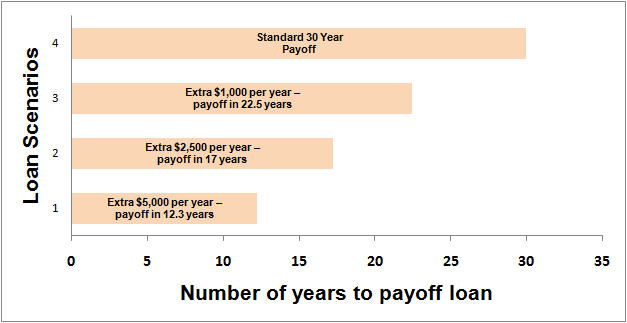
 Real estate has always been the fastest and safest investment vehicle to acquire wealth and reach millionaire status. But without a down payment your
Real estate has always been the fastest and safest investment vehicle to acquire wealth and reach millionaire status. But without a down payment your 