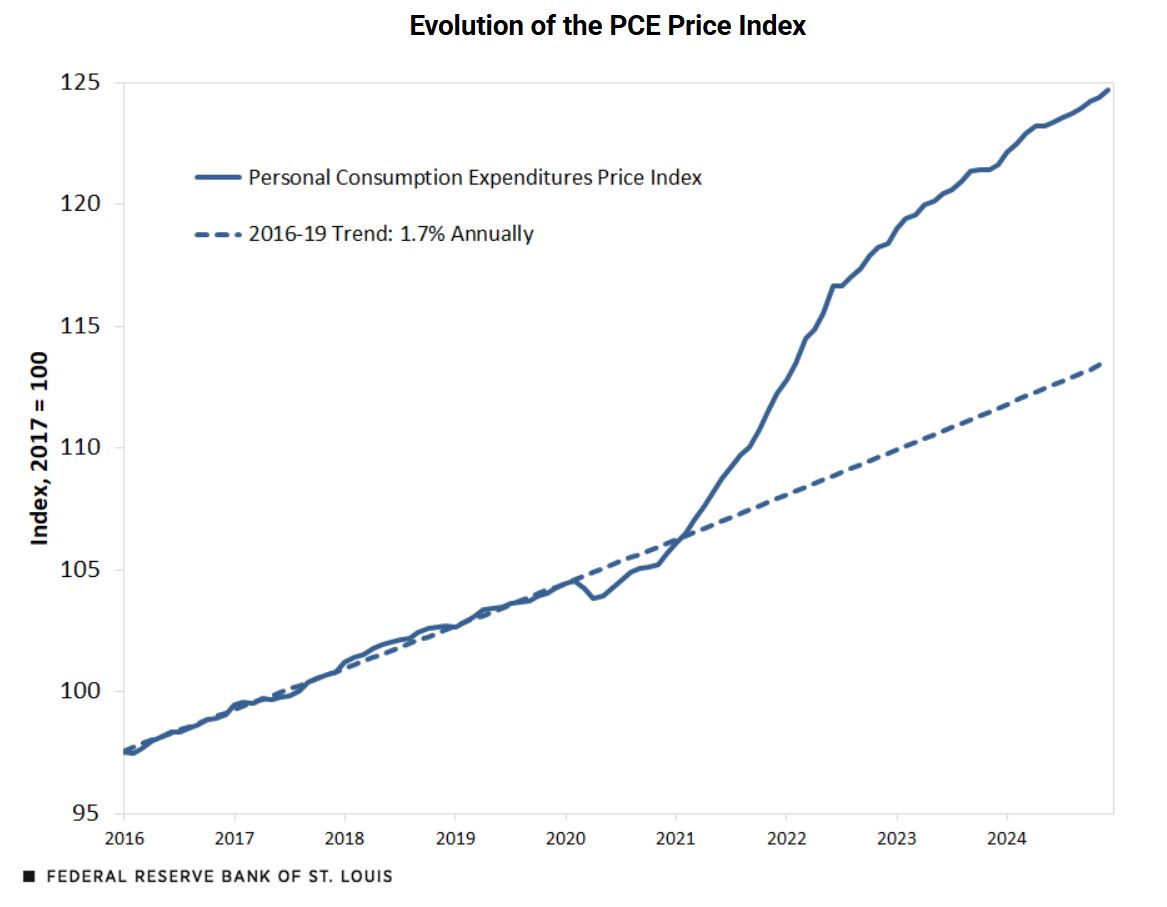
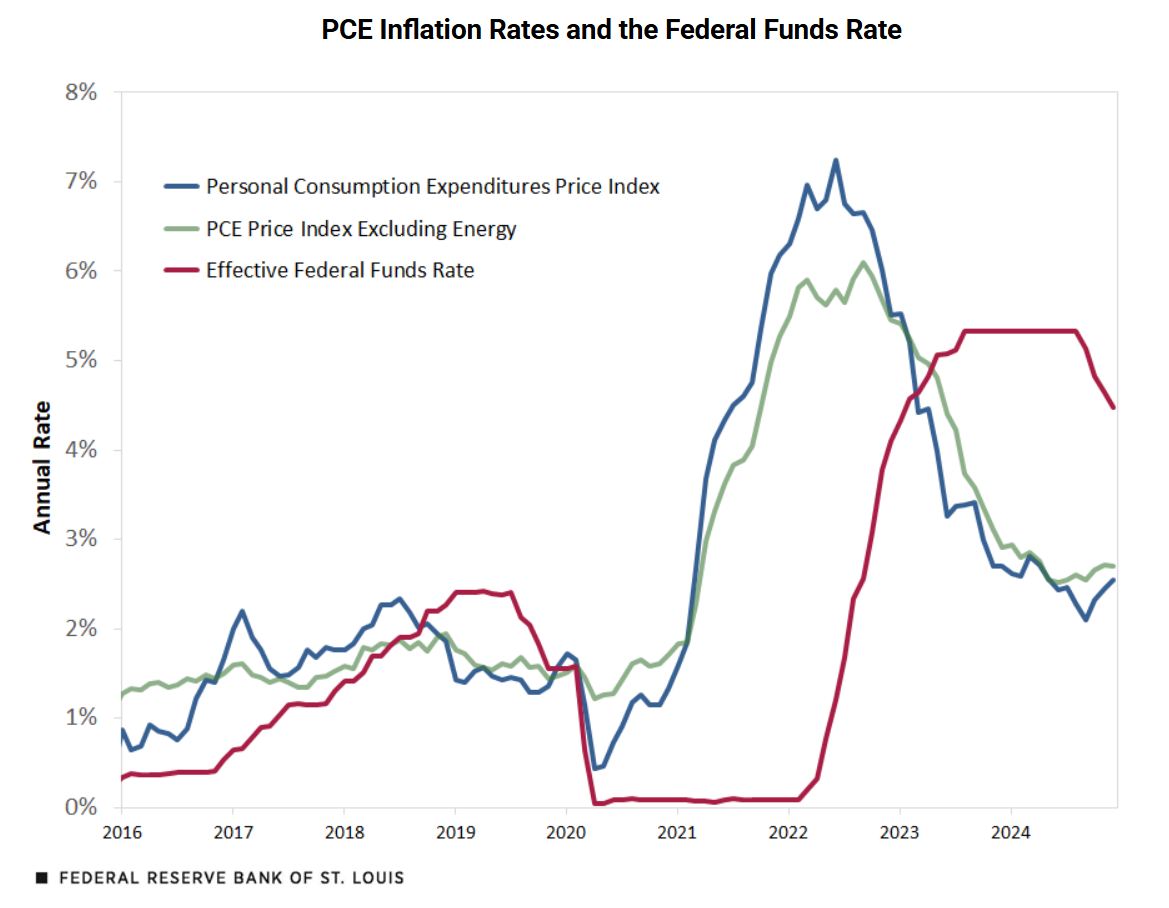
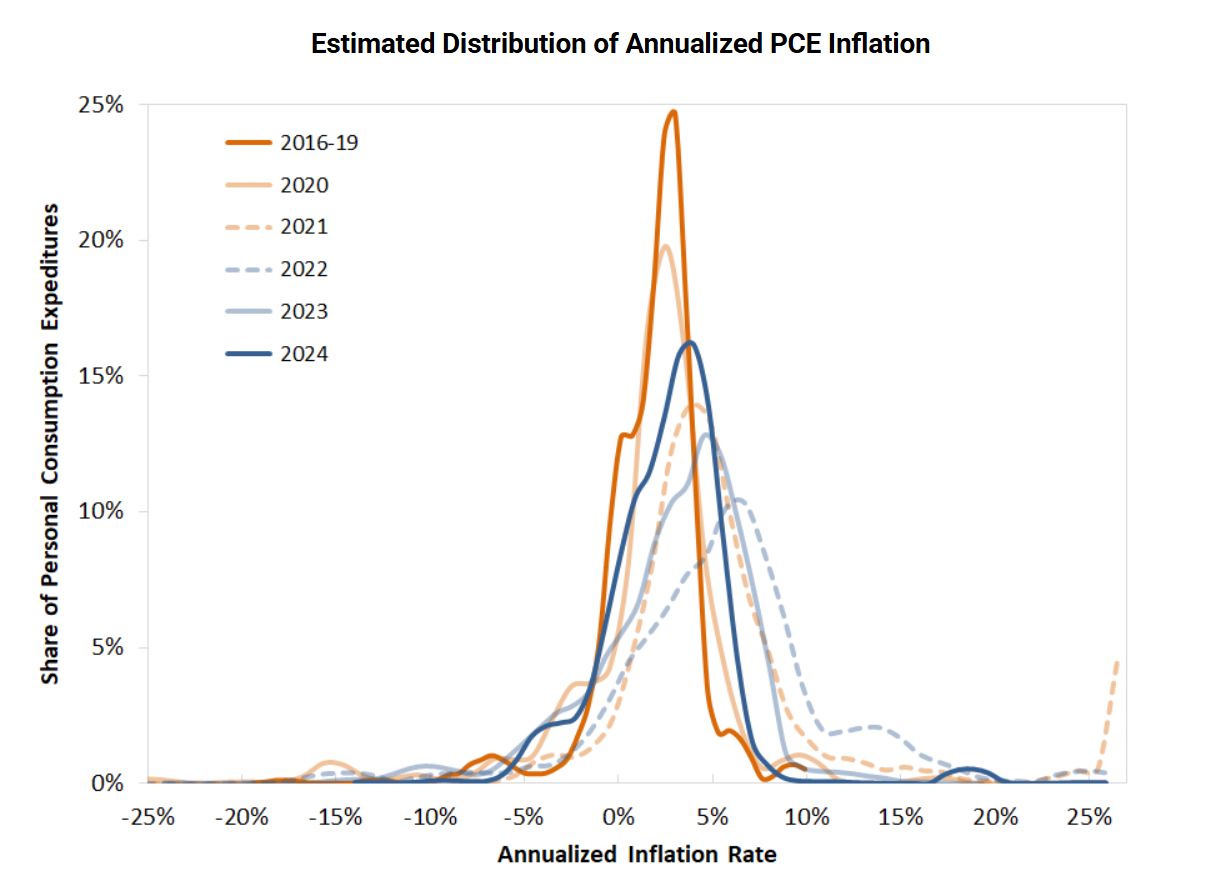
Have you ever gone to the grocery store and noticed that your favorite snacks suddenly cost a lot more? Or maybe you're thinking about buying a new TV, but the prices seem to have jumped up? These price increases, what we call inflation, can really hit our wallets hard. And lately, there's been a lot of talk about something called tariffs – taxes on goods coming into our country from other places.
Tariffs Impact Housing Market: Homebuilders Sound Alarm on Rising Costs
Dreaming of a new home? Maybe you’re picturing fresh paint, that new house smell, and finally having that extra space you’ve always wanted. But that dream might just be getting a little pricier, and here’s why: homebuilders are sounding the alarm because the cost of building materials is going up thanks to the new tariffs slapped on goods from Canada and Mexico by the Trump administration. These tariffs, intended to pressure our neighbors to tighten up border security, are having an unintended side effect right here at home – potentially making new houses more expensive for everyday folks like you and me.
Tariffs on Trade Partners Hit Home
So, what exactly happened? Well, President Trump put in place a hefty 25% tariff on goods coming in from both Canada and Mexico. This isn't just a minor tweak; it’s a significant tax on a wide range of products that cross our borders. The idea, as the White House explains it, is to push Canada and Mexico to do more to control the flow of illegal drugs and unauthorized immigration into the United States. Alongside these tariffs, there's also an additional 10% tariff on goods from China, adding another layer to this trade tension.
But here’s the rub – these tariffs hit industries that rely heavily on imports, and homebuilding is right at the top of that list. Buddy Hughes, the Chairman of the National Association of Homebuilders, put it plainly when he spoke to Realtor.com®. He warned that “this move to raise tariffs by 25% on Canadian and Mexican goods will harm housing affordability.” It's not just a vague worry; it's a direct hit to the wallet for anyone looking to buy a new home.
Think about it – when the price of lumber and other essential building materials goes up, who do you think ultimately pays? It's going to be the folks buying the houses. As Hughes pointed out, “tariffs on lumber and other building materials increase the cost of construction and discourage new development, and consumers end up paying for the tariffs in the form of higher home prices.” He's urging the Trump administration to reconsider these tariffs, emphasizing the need to keep housing affordable and to work together to boost home production.
Where Do Building Materials Come From Anyway?
You might be wondering, why are Canada and Mexico so important when it comes to building houses in the U.S.? Well, turns out, we depend on them quite a bit. Industry figures show that about 70% of the dimensional lumber used to build our homes comes from Canada. Think about the wood framing, the floors, the roofs – a lot of that starts in Canadian forests. Similarly, Mexico is a major source for drywall gypsum, that material that makes up the walls inside our houses. While China also supplies some fixtures and finishes, Canada and Mexico are the real heavy hitters when it comes to the raw materials of home construction.
This reliance on imports means that when tariffs are imposed on these countries, it’s not just a distant trade dispute – it directly impacts the cost of building a home right here in America. It’s like putting a tax directly on the materials that go into the walls and roofs over our heads.
The Ripple Effect on Home Prices
Danielle Hale, the Chief Economist at Realtor.com, paints a pretty clear picture of what this means for the housing market. According to her, builders are facing a tough choice: “Rising costs due to tariffs on imports will leave builders with few options. They can choose to pass higher costs along to consumers, which will mean higher home prices, or try to use less of these materials, which will mean smaller homes.”
Neither option is great for homebuyers. If builders pass the costs on, suddenly that dream home becomes even more out of reach for many families. Especially at a time when housing affordability is already a major concern in many parts of the country. Or, if builders try to cut costs by using less material, we could end up seeing smaller houses, maybe with fewer features, just to keep prices somewhat manageable. It’s a squeeze either way.
Hale also points out that the impact could go beyond just new homes. For a while now, the price difference between new construction and existing homes had been getting smaller in some areas. But these tariffs could reverse that trend. “The premium on new construction homes that had been shrinking in many markets according to Realtor.com data could begin to rise again, or we may see buyer's willingness to pay rise for existing homes as newly built homes get pricier—which would mean rising prices for existing homes, too,” she explains.
So, it’s not just about the price of new homes potentially going up. If new homes become more expensive, it could push up demand and prices for existing homes as well. It’s a ripple effect that could impact the entire housing market.
And it's not just buying a home that could be affected. Hale also notes that those home renovation projects we’ve been dreaming about might also get more expensive. “We may also see a lower appetite for major remodeling projects that would rely on these tariff-affected inputs, hamstringing the ability of consumers to remake their homes to fit their current needs,” she says. Want to finally redo that kitchen or bathroom? The tariffs on imported materials could make those projects cost more and potentially put them on hold for many homeowners.
Trump's Solution: More Logging
President Trump has acknowledged that we rely too much on foreign lumber. His solution? He wants to boost domestic timber production. He even signed executive orders aimed at ramping up logging in national forests. The idea is that by cutting down more trees here in the U.S., we can reduce our reliance on Canadian lumber and hopefully bring down building costs.
Now, environmental groups aren’t too thrilled about this idea, and it's understandable why. Expanding logging in national forests raises concerns about habitat loss, deforestation, and the impact on ecosystems. However, the Trump administration argues that more domestic logging is the answer to bring down building costs and lessen our dependence on Canadian lumber. It’s a complex issue with different sides and valid points.
“A Drug War, Not a Trade War”?
Adding another layer to this whole situation, a senior White House official told Realtor.com that these tariffs aren't really about trade in the long run. They are, according to this official, “a national security measure narrowly targeted at halting the international drug trade and illegal immigration, and are not intended as a long-term economic policy.” The official even suggested that the tariffs on Canada and Mexico might not last long enough to really mess with the housing supply chain, since building a house takes months anyway.
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick echoed this sentiment, telling CNBC on Tuesday morning, “This is not a trade war, this is a drug war.” He mentioned an April 2nd deadline for a report on trade deals, suggesting there will be discussions on how to “reset trade correctly.”
However, words are one thing, and actions are another. Canada and Mexico didn’t take these tariffs lying down. They swiftly retaliated by slapping their own tariffs on U.S. goods. This tit-for-tat tariff battle raises the specter of a full-blown trade war, which nobody really wants. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau didn't mince words, calling the tariffs “a very dumb thing to do” directly addressing President Trump. Ontario Premier Doug Ford even threatened to cut off electricity to several U.S. states, showing just how tense things are getting.
Market Jitters and Uncertainty
The financial markets aren’t exactly cheering about all this trade drama either. The S\&P 500, a key measure of stock market performance, dropped about 3.7% in the week as it became clear Trump was going ahead with these tariffs. Paul Ashworth, Chief North America Economist for Capital Economics, noted that “Markets have predictably reacted badly, since this raises the risk that Trump will also follow through on his threats to impose reciprocal country-specific tariffs soon, including a proposed 25% on imports from the EU.” The fear is that this could be just the beginning of a much wider trade conflict, impacting not just housing but the entire economy.
Remember, this all started back in February when Trump first announced these tariffs. He initially suspended them for 30 days for Canada and Mexico, hoping they would step up border enforcement. He did, however, impose a 10% tariff on China last month, bringing the total to 20% now. The focus with China is on cracking down on the production of chemicals used to make fentanyl, a deadly drug.
President Trump is expected to address Congress and the nation soon, and it’s anticipated he’ll talk about the economy and inflation. It will be interesting to see how he addresses these tariffs and the concerns about rising costs, especially in the housing market.
The Bottom Line for Homebuyers
So, where does all of this leave us? Well, it's still quite uncertain how long these tariffs will last and what the ultimate impact will be. But one thing is clear: homebuilders are worried. They’re warning that these tariffs on Canada and Mexico are likely to increase building costs, which could translate to higher prices for new homes and potentially even impact the broader housing market and home renovation projects. Whether this is a short-term blip or a more lasting shift remains to be seen. But if you're in the market for a new home, it’s definitely something to keep an eye on. The dream of homeownership might just be getting a little more expensive in the face of these trade tensions.
Navigate Economic Uncertainty with
Norada Real Estate Investments
Whether it's recession or inflation, turnkey real estate offers stability and consistent returns.
Diversify your portfolio with ready-to-rent properties designed to withstand economic fluctuations.
Speak with our expert investment counselors (No Obligation):
(800) 611-3060
Read More:
- Will Higher Tariffs Lead to Inflation and Higher Interest Rates in 2025?
- Will the Fed Achieve Its 2% Inflation Target in 2025: The Road Ahead
- Are We in a Recession or Inflation: Forecast for 2025
- Inflation's Impact on Home Prices & Mortgages: What to Expect in 2025
- Interest Rates vs. Inflation: Is the Fed Winning the Fight?
- Is Fed Taming Inflation or Triggering a Housing Crisis?
- Will Inflation Go Down Below 2% in 2025: Economic Forecast
- How To Invest in Real Estate During a Recession?
- Will There Be a Recession in 2025?
- When Will This Recession End?
- Should I Buy a House Now or Wait for Recession?