Will interest rates drop in 2024? The answer to this pivotal question holds significant implications for investors, homeowners, businesses, and the overall financial landscape. Before we can peer into the future, it's essential to understand the complex terrain upon which interest rates are set.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a pivotal role in determining these rates. The primary objective is to strike a delicate balance between stimulating economic growth and curbing inflation.
Key Factors Influencing Interest Rate Cuts or Rise:
- Economic Growth: Robust economic growth often prompts central banks to raise rates to prevent overheating.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can lead to higher interest rates to maintain the purchasing power of a nation's currency.
- Central Bank Policies: Decisions made by central banks, including changes in the federal funds rate, have a direct impact on interest rates.
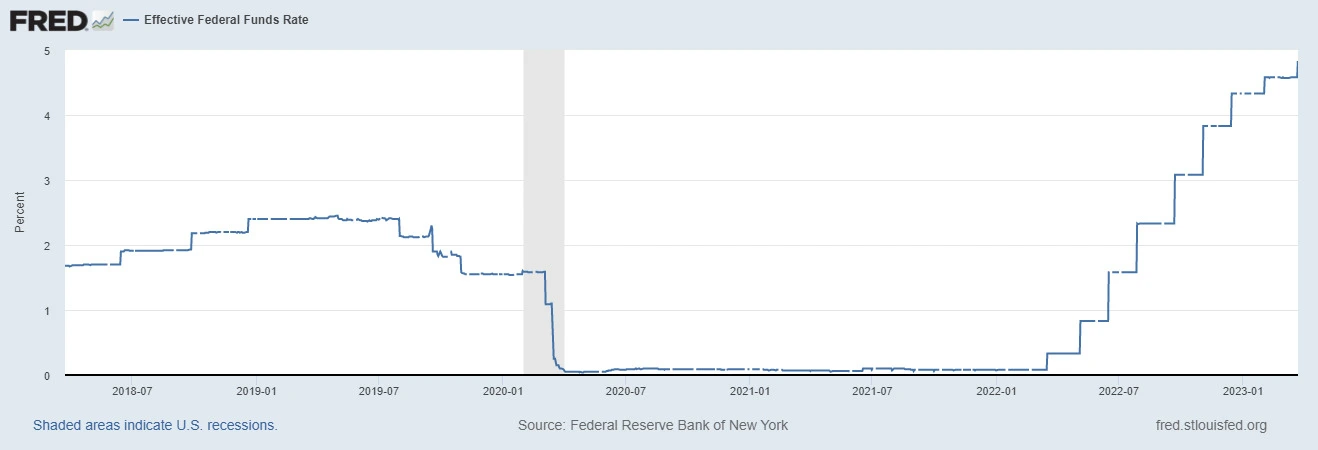
The Federal Reserve has been on a tightening cycle since 2019, raising the federal funds rate from a record low of 0.25% to a 22-year high of 5.5% in September 2023. The Fed's main goal is to cool down the inflationary pressures that have been building up in the economy due to the pandemic recovery, supply chain disruptions, and fiscal stimulus.
However, many economists and market participants expect that the Fed will soon reach the peak of its policy tightening and start to lower interest rates in 2024. According to a survey by Bankrate, 94% of economists say the Fed could begin cutting interest rates in 2024, while 6% expect the Fed to cut rates in 2025 or later. The
Fed's own projections also show that rate cuts are not on the table until at least 2024, with a median forecast of 5.1% for the end of 2023 and 3.9% for the end of 2024.
Will Interest Rates Go Down in 2024: Factors Leading to Potential Interest Rate Cuts
What are the factors that could lead the Fed to cut interest rates in 2024? One of them is the expected slowdown in economic growth as the effects of fiscal stimulus fade and the pandemic-related disruptions ease. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects that the US economy will grow by 6.2% in 2023, but only by 2.8% in 2024.
Another factor is the expected decline in inflation as supply and demand imbalances are resolved and commodity prices moderate. The Fed expects inflation to average 3.7% in 2023, but to fall to 2.2% in 2024.
Of course, there are also risks and uncertainties that could alter the Fed's plans. For example, if inflation proves to be more persistent or higher than expected, the Fed may have to raise interest rates further or faster than anticipated. Conversely, if the economy faces a negative shock or a downturn, the Fed may have to cut interest rates sooner or deeper than projected.
As long as core inflation remains significantly above the Federal Reserve's target, the Fed Funds rate is usually expected to rise. The Fed's primary instrument for controlling inflation is its ability to influence interest rates. Based on what it sees in the economy, the Fed can raise or lower its benchmark rate, known as the federal funds rate. The federal funds rate affects how much banks and other financial organizations pay to borrow, which in turn affects businesses and people.
Implications of Fed's Interest Rate Decisions
Fed wants to concentrate on slowing demand. It wants fewer people to buy new automobiles or put down bids on houses, lowering costs. When the Fed raises its benchmark interest rate, all types of financing become more expensive. Mortgage rates rise. Auto loans are no exception. Over time, this helps supply and demand rebalance to bring down core inflation.
The Federal Reserve is doing its share to combat inflation by boosting interest rates. While the Fed's goals are excellent, its actions are burdening consumers by increasing the cost of borrowing money. The Federal Reserve hopes to discourage customers from spending money by hiking interest rates. As a result, the gap between supply and demand can be narrowed, potentially leading to lower levels of inflation.
The Fed's interest rate decisions have important implications for consumers and businesses, as they affect the cost and availability of credit for various purposes. For example, mortgage rates are influenced by the 10-year Treasury yield, which reflects market expectations of future Fed policy.
The Bankrate survey predicts that the 10-year Treasury yield will ease somewhat over the next 12 months, edging down to 3.99% from its current level of 4.56%. However, this is still much higher than the historical average of around 2%, and could make homeownership less affordable for many borrowers.
Other types of loans, such as car loans, home equity loans, and credit cards, are more directly linked to the federal funds rate or other short-term interest rates. These rates are expected to remain high until the Fed starts to cut them in 2024 or later. This means that consumers will have to pay more interest on their existing debt or new borrowing, which could reduce their spending power and savings.
The bottom line is that interest rates are likely to stay elevated for some time until the Fed is confident that inflation is under control and the economy is on a sustainable path. Consumers and businesses should plan accordingly and take advantage of any opportunities to lock in lower rates or refinance their debt if possible.
Factors Which Impact Interest Rates
Interest rates are currently at their highest levels in decades, and many people are wondering when they will start to come down. There is no easy answer to this question, as it depends on a number of factors, including the path of inflation, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy, the overall state of the economy, and the ongoing war in Ukraine.
Inflation: Inflation is currently at a 40-year high, and the Federal Reserve is raising interest rates in an effort to bring it under control. Once inflation starts to come down, the Fed is likely to slow down or even stop raising rates.
This could lead to a decline in interest rates in 2024. However, it is important to note that the war in Ukraine has exacerbated inflationary pressures, and it is difficult to predict when inflation will start to come down. If inflation remains high for a prolonged period of time, the Fed may be forced to keep interest rates higher than expected in 2024.
Economic growth: Economic growth is expected to slow in 2023, and there is a risk of a recession. If the economy does enter a recession, the Fed is likely to cut interest rates in an effort to stimulate economic activity. This would also lead to a decline in interest rates in 2024. However, the war in Ukraine has also increased the risk of a global recession.
If the global economy does contract, it could lead to lower interest rates in 2024, as central banks around the world try to support economic growth.
Global economic conditions: The global economy is also facing a number of other challenges, including the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and the disruption of global supply chains. These challenges could lead to higher interest rates in 2024, as central banks around the world try to combat inflation and support economic growth.
However, it is also possible that these challenges will lead to a slowdown in global economic growth. If this happens, it could lead to lower interest rates in 2024.
The Federal Reserve's balance sheet: The Federal Reserve has been reducing its balance sheet since November 2021. This process is known as quantitative tightening (QT). QT is likely to put upward pressure on interest rates in 2023 and 2024. However, the Fed may be forced to slow down or even stop QT if the economy weakens or if inflation remains high. If this happens, it could lead to lower interest rates in 2024.
What economists are saying
Most economists expect interest rates to start falling in 2024, but there is a wide range of forecasts. Some economists predict a more modest decline, while others anticipate a more significant drop. However, it is important to note that economists have a notoriously poor track record of forecasting interest rates. This is because interest rates are influenced by a complex set of factors that are difficult to predict.
What does it mean for you?
If interest rates do start to fall in 2024, it will be good news for borrowers. Lower interest rates can make it cheaper to buy a home, refinance a mortgage, or take out a personal loan. However, it is important to note that interest rates are just one factor that affects the cost of borrowing. Other factors, such as your credit score and debt-to-income ratio, can also play a role. If you are considering borrowing money, it is important to shop around and compare rates from different lenders. You should also talk to a financial advisor to get personalized advice.
Additional factors to consider
In addition to the factors mentioned above, there are a few other things to keep in mind when thinking about interest rates in 2024:
- The war in Ukraine: The war in Ukraine has had a significant impact on the global economy, and it is difficult to predict how long it will last. If the war continues for a prolonged period of time, it could lead to higher interest rates in 2024.
- The Federal Reserve's leadership: The Federal Reserve is currently led by Jerome Powell. Powell's term as Chair of the Fed is set to expire in February 2026. If President Biden does not reappoint Powell, it could lead to a change in the Fed's monetary policy, which could affect interest rates in 2024.
- Congressional action: Congress has the power to influence the Federal Reserve's monetary policy. For example, Congress could pass legislation that would require the Fed to keep interest rates low.
Overall, the Fed's data-driven strategy signals that interest rate decisions will be contingent on incoming economic indicators and inflationary developments. As the global economy continues its recovery from the pandemic's impact, investors, businesses, and consumers should closely monitor economic data and the Fed's actions to make informed decisions in a dynamic and evolving financial landscape.
Will Car Interest Rates Go Down in 2024?
If you are planning to buy a car in the next few years, you might be wondering how the interest rates will affect your financing options. Interest rates are influenced by many factors, such as the Federal Reserve's monetary policy, inflation, supply and demand, and market conditions.
The Federal Reserve has been raising the federal funds rate, which is the rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans, since early 2022. The Fed uses this rate to control inflation and stimulate or slow down the economy. The federal funds rate affects other interest rates, such as auto loan rates, which are usually higher than the Fed rate.
According to Bankrate, the average interest rate for a new car loan was 5.9% in November 2023, while the average rate for a used car loan was 6.75%. These rates are higher than the pre-pandemic levels of around 4.5% and 5.5%, respectively.
So, will auto loan rates go down in 2024? The answer is not clear-cut, but there are some projections and trends that can help you make an informed decision.
Auto Loan Rate Forecast for 2024
One factor to consider is the Fed's outlook for the future. Last year, the Fed indicated that it expects the federal funds rate to fall to 4.1% by the end of 2024 after reaching the 5.1% mark by the end of 2023. This means that the Fed may stop raising rates or even lower them in 2024, depending on how the economy performs.
Another factor to consider is the supply and demand of cars. The pandemic and the chip shortage have caused a tight inventory of new and used cars, driving up their prices and demand. However, there are also some factors that could keep car interest rates high or even increase them in 2024.
One of them is inflation, which is the general rise in prices of goods and services over time. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money and makes borrowing more expensive. The Fed tries to keep inflation around 2%, but it has been higher than that in recent months due to supply chain disruptions and pent-up demand.
Another factor is your credit score, which is a measure of your creditworthiness based on your payment history, debt level, and other factors. Your credit score affects the interest rate you qualify for when you apply for a car loan. Generally, the higher your credit score, the lower your interest rate. However, if you have a poor credit history, you may face higher rates or difficulty getting approved for a loan.
Thus, car interest rates may go down in 2024 if the Fed lowers its target rate, car prices drop, and inflation eases. However, they may also stay high or increase if the opposite happens. Therefore, it is important to monitor the market conditions and your credit situation before you decide to buy a car in 2024.
References:
- https://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents.htm
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/EFFR#