In this blog post, we will be reviewing the list of failed banks in the United States. It's never good news when we hear about a bank failure, and unfortunately, there have been quite a few in the United States over the years. From Washington Mutual and IndyMac in 2008 to Guaranty Bank and First NBC Bank in 2017, these failures can have a big impact on customers, employees, and the economy as a whole. While there are often warning signs leading up to a bank failure, it can still be a shock and a disappointment to those affected.2
It's important to remember, though, that the government has systems in place to help protect customers' deposits and ensure that the banking industry remains stable overall. Banks are an important part of our financial system, but unfortunately, they can fail from time to time. There are a few reasons why this might happen. One common cause is undercapitalization, which means that the bank doesn't have enough money to cover its obligations.
Another factor is loan quality – if a bank makes too many bad loans, it can end up losing a lot of money. Additionally, losses on investment securities can also contribute to a bank's failure. When a bank fails, it can have a ripple effect on the economy and on the people who have accounts with that bank. That's why it's important for regulators to keep a close eye on banks and step in when necessary to prevent failures from happening.
ALSO READ: Which Banks Are in Danger of Failing or Collapse?
Bank Failures This Week – The Citizens Bank, Sac City, Iowa
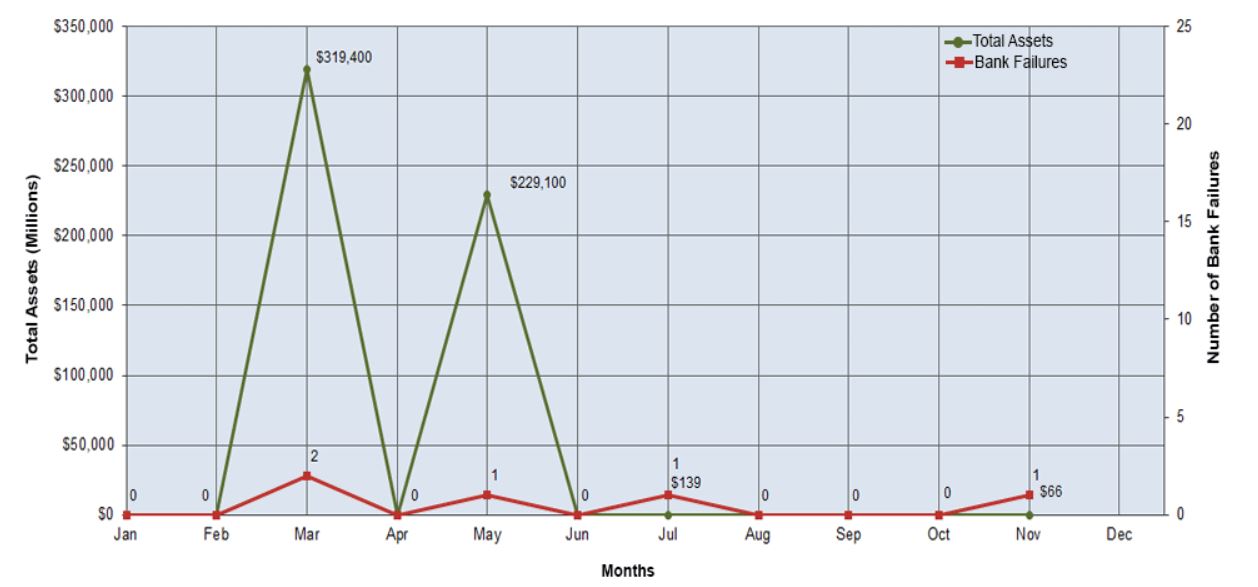
The latest bank that collapsed was The Citizens Bank, Sac City, Iowa. Citizens Bank's closure marks the fifth bank failure in the nation in 2023. The last bank failure in Iowa was Polk County Bank in Johnston, which occurred on November 18, 2011, highlighting the rarity of such events in the state.
It faced closure as the Iowa Division of Banking took action. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) was appointed as the receiver to safeguard the interests of depositors. In a move to ensure depositors' safety, the FDIC forged a Purchase and Assumption Agreement with Iowa Trust & Savings Bank, Emmetsburg, Iowa. Iowa Trust & Savings Bank would take on the responsibility of securing all the deposits of Citizens Bank.
The transition for customers of Citizens Bank would be smooth and efficient. The two branches of Citizens Bank will reopen as branches of Iowa Trust & Savings Bank during normal business hours, starting on Monday. Depositors can access their funds through check writing or ATM and debit card usage throughout the weekend. Checks drawn on the bank will continue to be processed, and loan customers should make their payments as usual.
Depositors of Citizens Bank need not worry about changing their banking relationship to maintain their deposit insurance coverage. They will automatically become depositors of Iowa Trust & Savings Bank, ensuring continuity in their financial security.
As of September 30, 2023, Citizens Bank held approximately $66 million in total assets and $59 million in total deposits. Iowa Trust & Savings Bank has also agreed to purchase most of the failed bank's assets, securing the financial well-being of its customers.
The FDIC estimates that the cost to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) will be $14.8 million. This resolution by Iowa Trust & Savings Bank is considered the least costly option compared to other alternatives, emphasizing the importance of the DIF in protecting the nation's bank deposits.
To prevent bank failures, regulators closely monitor banks and enforce regulations to ensure that they are adequately capitalized and managing risk appropriately. In addition, deposit insurance programs such as the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in the United States help protect customers' deposits in the event of a bank failure.
ALSO READ: Banking Crisis Explained: Causes of Bank Collapse & its Prevention
List of Banks Examined for CRA Compliance – November 2023
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) recently released its list of state nonmember banks that were evaluated for compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA). This list, which covers evaluation ratings assigned by the FDIC in August 2023, plays a crucial role in promoting responsible banking practices and community development.
Understanding the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA)
The CRA, enacted in 1977, serves as a cornerstone of ensuring that insured banks and thrifts contribute to the betterment of their communities. This law encourages financial institutions to meet the credit needs of local communities, particularly those in low- and moderate-income neighborhoods, all while maintaining safe and sound operations.
Mandatory Public Disclosure
In 1989, as part of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act (FIRREA), the Congress mandated the public disclosure of evaluation and rating reports for each bank or thrift that undergoes a CRA examination on or after July 1, 1990. This transparency ensures that banks are held accountable for their community reinvestment efforts.
Accessing the Evaluation Results
If you're interested in obtaining information about state nonmember banks' CRA evaluations, the FDIC provides a consolidated list that has been publicly available since July 1, 1990. This list includes the rating for each bank. You can access this information online or obtain a hard copy from the FDIC's Public Information Center at 3501 Fairfax Drive, Room E-1002, Arlington, VA 22226. For inquiries, you can contact them at 877-275-3342 or 703-562-2200.
Requesting Individual Bank Evaluations
If you need the CRA evaluation for a specific bank, it's good to know that these reports are available directly from the bank itself. The law requires banks to make this information available upon request. You can also request these evaluations from the FDIC's Public Information Center, ensuring transparency and accessibility for the public.
The release of the FDIC's list of banks evaluated for CRA compliance underscores the importance of transparency and accountability in the banking industry. The Community Reinvestment Act continues to be a vital tool in promoting responsible banking practices and ensuring that financial institutions are actively contributing to the well-being of their local communities.
With public access to these evaluation reports, consumers and communities can make informed decisions about their banking relationships and hold banks accountable for their community reinvestment efforts. It's a step towards a more equitable and responsible banking sector.
List of Recent Failed Banks [2021 – 2023]
|
Bank Name |
City |
State |
Cert |
Acquiring Institution |
Closing Date |
Fund |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citizens Bank | Sac City | IA | 8758 | Iowa Trust & Savings Bank | November 3, 2023 | 10545 |
| Heartland Tri-State Bank | Elkhart | KS | 25851 | Dream First Bank, N.A. | July 28, 2023 | 10544 |
| First Republic Bank | San Francisco | CA | 59017 | JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. | May 1, 2023 | 10543 |
| Signature Bank | New York | NY | 57053 | Flagstar Bank, N.A. | March 12, 2023 | 10540 |
| Silicon Valley Bank | Santa Clara | CA | 24735 | First–Citizens Bank & Trust Company | March 10, 2023 | 10539 |
List of Recent Failed Banks [2015 – 2020]
| Bank Name | City | State | Acquiring Institution | Closing Date |
| Almena State Bank | Almena | KS | Equity Bank | October 23, 2020 |
| First City Bank of Florida | Fort Walton Beach | FL | United Fidelity Bank, fsb | October 16, 2020 |
| The First State Bank | Barboursville | WV | MVB Bank, Inc. | April 3, 2020 |
| Ericson State Bank | Ericson | NE | Farmers and Merchants Bank | February 14, 2020 |
| City National Bank of New Jersey | Newark | NJ | Industrial Bank | November 1, 2019 |
| Resolute Bank | Maumee | OH | Buckeye State Bank | October 25, 2019 |
| Louisa Community Bank | Louisa | KY | Kentucky Farmers Bank Corporation | October 25, 2019 |
| The Enloe State Bank | Cooper | TX | Legend Bank, N. A. | May 31, 2019 |
| Washington Federal Bank for Savings | Chicago | IL | Royal Savings Bank | December 15, 2017 |
| The Farmers and Merchants State Bank of Argonia | Argonia | KS | Conway Bank | October 13, 2017 |
| Fayette County Bank | Saint Elmo | IL | United Fidelity Bank, fsb | May 26, 2017 |
| Guaranty Bank, (d/b/a BestBank in Georgia & Michigan) | Milwaukee | WI | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | May 5, 2017 |
| First NBC Bank | New Orleans | LA | Whitney Bank | April 28, 2017 |
| Proficio Bank | Cottonwood Heights | UT | Cache Valley Bank | March 3, 2017 |
| Seaway Bank and Trust Company | Chicago | IL | State Bank of Texas | January 27, 2017 |
| Harvest Community Bank | Pennsville | NJ | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | January 13, 2017 |
| Allied Bank | Mulberry | AR | Today's Bank | September 23, 2016 |
| The Woodbury Banking Company | Woodbury | GA | United Bank | August 19, 2016 |
| First CornerStone Bank | King of Prussia | PA | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | May 6, 2016 |
| Trust Company Bank | Memphis | TN | The Bank of Fayette County | April 29, 2016 |
| North Milwaukee State Bank | Milwaukee | WI | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | March 11, 2016 |
| Hometown National Bank | Longview | WA | Twin City Bank | October 2, 2015 |
| The Bank of Georgia | Peachtree City | GA | Fidelity Bank | October 2, 2015 |
| Premier Bank | Denver | CO | United Fidelity Bank, fsb | July 10, 2015 |
| Edgebrook Bank | Chicago | IL | Republic Bank of Chicago | May 8, 2015 |
| Doral Bank | San Juan | PR | Banco Popular de Puerto Rico | February 27, 2015 |
| En Español | ||||
| Capitol City Bank & Trust Company | Atlanta | GA | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | February 13, 2015 |
| Highland Community Bank | Chicago | IL | United Fidelity Bank, fsb | January 23, 2015 |
| First National Bank of Crestview | Crestview | FL | First NBC Bank | January 16, 2015 |
List of Failed Banks [2013 – 2014]
| Bank Name | City | State | Acquiring Institution | Closing Date |
| Northern Star Bank | Mankato | MN | BankVista | 19-Dec-14 |
| Frontier Bank, FSB D/B/A El Paseo Bank | Palm Desert | CA | Bank of Southern California, N.A. | 07-Nov-14 |
| The National Republic Bank of Chicago | Chicago | IL | State Bank of Texas | 24-Oct-14 |
| NBRS Financial | Rising Sun | MD | Howard Bank | 17-Oct-14 |
| GreenChoice Bank, fsb | Chicago | IL | Providence Bank, LLC | 25-Jul-14 |
| Eastside Commercial Bank | Conyers | GA | Community & Southern Bank | 18-Jul-14 |
| The Freedom State Bank | Freedom | OK | Alva State Bank & Trust Company | 27-Jun-14 |
| Valley Bank | Fort Lauderdale | FL | Landmark Bank, National Association | 20-Jun-14 |
| Valley Bank | Moline | IL | Great Southern Bank | 20-Jun-14 |
| Slavie Federal Savings Bank | Bel Air | MD | Bay Bank, FSB | 30-May-14 |
| Columbia Savings Bank | Cincinnati | OH | United Fidelity Bank, fsb | 23-May-14 |
| AztecAmerica Bank | Berwyn | IL | Republic Bank of Chicago | 16-May-14 |
| Allendale County Bank | Fairfax | SC | Palmetto State Bank | 25-Apr-14 |
| Vantage Point Bank | Horsham | PA | First Choice Bank | 28-Feb-14 |
| Millennium Bank, National Association | Sterling | VA | WashingtonFirst Bank | 28-Feb-14 |
| Syringa Bank | Boise | ID | Sunwest Bank | 31-Jan-14 |
| The Bank of Union | El Reno | OK | BancFirst | 24-Jan-14 |
| DuPage National Bank | West Chicago | IL | Republic Bank of Chicago | 17-Jan-14 |
| Texas Community Bank, National Association | The Woodlands | TX | Spirit of Texas Bank, SSB | 13-Dec-13 |
| Bank of Jackson County | Graceville | FL | First Federal Bank of Florida | 30-Oct-13 |
| First National Bank also operating as The National Bank of El Paso | Edinburg | TX | PlainsCapital Bank | 13-Sep-13 |
| The Community's Bank | Bridgeport | CT | No Acquirer | 13-Sep-13 |
| Sunrise Bank of Arizona | Phoenix | AZ | First Fidelity Bank, National Association | 23-Aug-13 |
| Community South Bank | Parsons | TN | CB&S Bank, Inc. | 23-Aug-13 |
| Bank of Wausau | Wausau | WI | Nicolet National Bank | 09-Aug-13 |
| First Community Bank of Southwest Florida (also operating as Community Bank of Cape Coral) | Fort Myers | FL | C1 Bank | 02-Aug-13 |
| Mountain National Bank | Sevierville | TN | First Tennessee Bank, National Association | 07-Jun-13 |
| 1st Commerce Bank | North Las Vegas | NV | Plaza Bank | 06-Jun-13 |
| Banks of Wisconsin d/b/a Bank of Kenosha | Kenosha | WI | North Shore Bank, FSB | 31-May-13 |
| Central Arizona Bank | Scottsdale | AZ | Western State Bank | 14-May-13 |
| Sunrise Bank | Valdosta | GA | Synovus Bank | 10-May-13 |
| Pisgah Community Bank | Asheville | NC | Capital Bank, N.A. | 10-May-13 |
| Douglas County Bank | Douglasville | GA | Hamilton State Bank | 26-Apr-13 |
| Parkway Bank | Lenoir | NC | CertusBank, National Association | 26-Apr-13 |
| Chipola Community Bank | Marianna | FL | First Federal Bank of Florida | 19-Apr-13 |
| Heritage Bank of North Florida | Orange Park | FL | FirstAtlantic Bank | 19-Apr-13 |
| First Federal Bank | Lexington | KY | Your Community Bank | 19-Apr-13 |
| Gold Canyon Bank | Gold Canyon | AZ | First Scottsdale Bank, National Association | 05-Apr-13 |
| Frontier Bank | LaGrange | GA | HeritageBank of the South | 08-Mar-13 |
| Covenant Bank | Chicago | IL | Liberty Bank and Trust Company | 15-Feb-13 |
| 1st Regents Bank | Andover | MN | First Minnesota Bank | 18-Jan-13 |
| Westside Community Bank | University Place | WA | Sunwest Bank | 11-Jan-13 |
List of Failed Banks [2011 – 2012]
| Bank Name | City | State | Acquiring Institution | Closing Date |
| Community Bank of the Ozarks | Sunrise Beach | MO | Bank of Sullivan | 14-Dec-12 |
| Hometown Community Bank | Braselton | GA | CertusBank, National Association | 16-Nov-12 |
| Citizens First National Bank | Princeton | IL | Heartland Bank and Trust Company | 02-Nov-12 |
| Heritage Bank of Florida | Lutz | FL | Centennial Bank | 02-Nov-12 |
| NOVA Bank | Berwyn | PA | No Acquirer | 26-Oct-12 |
| Excel Bank | Sedalia | MO | Simmons First National Bank | 19-Oct-12 |
| First East Side Savings Bank | Tamarac | FL | Stearns Bank N.A. | 19-Oct-12 |
| GulfSouth Private Bank | Destin | FL | SmartBank | 19-Oct-12 |
| First United Bank | Crete | IL | Old Plank Trail Community Bank, National Association | 28-Sep-12 |
| Truman Bank | St. Louis | MO | Simmons First National Bank | 14-Sep-12 |
| First Commercial Bank | Bloomington | MN | Republic Bank & Trust Company | 07-Sep-12 |
| Waukegan Savings Bank | Waukegan | IL | First Midwest Bank | 03-Aug-12 |
| Jasper Banking Company | Jasper | GA | Stearns Bank N.A. | 27-Jul-12 |
| Second Federal Savings and Loan Association of Chicago | Chicago | IL | Hinsdale Bank & Trust Company | 20-Jul-12 |
| Heartland Bank | Leawood | KS | Metcalf Bank | 20-Jul-12 |
| First Cherokee State Bank | Woodstock | GA | Community & Southern Bank | 20-Jul-12 |
| Georgia Trust Bank | Buford | GA | Community & Southern Bank | 20-Jul-12 |
| The Royal Palm Bank of Florida | Naples | FL | First National Bank of the Gulf Coast | 20-Jul-12 |
| Glasgow Savings Bank | Glasgow | MO | Regional Missouri Bank | 13-Jul-12 |
| Montgomery Bank & Trust | Ailey | GA | Ameris Bank | 06-Jul-12 |
| The Farmers Bank of Lynchburg | Lynchburg | TN | Clayton Bank and Trust | 15-Jun-12 |
| Security Exchange Bank | Marietta | GA | Fidelity Bank | 15-Jun-12 |
| Putnam State Bank | Palatka | FL | Harbor Community Bank | 15-Jun-12 |
| Waccamaw Bank | Whiteville | NC | First Community Bank | 08-Jun-12 |
| Farmers' and Traders' State Bank | Shabbona | IL | First State Bank | 08-Jun-12 |
| Carolina Federal Savings Bank | Charleston | SC | Bank of North Carolina | 08-Jun-12 |
| First Capital Bank | Kingfisher | OK | F & M Bank | 08-Jun-12 |
| Alabama Trust Bank, National Association | Sylacauga | AL | Southern States Bank | 18-May-12 |
| Security Bank, National Association | North Lauderdale | FL | Banesco USA | 04-May-12 |
| Palm Desert National Bank | Palm Desert | CA | Pacific Premier Bank | 27-Apr-12 |
| Plantation Federal Bank | Pawleys Island | SC | First Federal Bank | 27-Apr-12 |
| Inter Savings Bank, fsb D/B/A InterBank, fsb | Maple Grove | MN | Great Southern Bank | 27-Apr-12 |
| HarVest Bank of Maryland | Gaithersburg | MD | Sonabank | 27-Apr-12 |
| Bank of the Eastern Shore | Cambridge | MD | No Acquirer | 27-Apr-12 |
| Fort Lee Federal Savings Bank, FSB | Fort Lee | NJ | Alma Bank | 20-Apr-12 |
| Fidelity Bank | Dearborn | MI | The Huntington National Bank | 30-Mar-12 |
| Premier Bank | Wilmette | IL | International Bank of Chicago | 23-Mar-12 |
| Covenant Bank & Trust | Rock Spring | GA | Stearns Bank, N.A. | 23-Mar-12 |
| New City Bank | Chicago | IL | No Acquirer | 09-Mar-12 |
| Global Commerce Bank | Doraville | GA | Metro City Bank | 02-Mar-12 |
| Home Savings of America | Little Falls | MN | No Acquirer | 24-Feb-12 |
| Central Bank of Georgia | Ellaville | GA | Ameris Bank | 24-Feb-12 |
| SCB Bank | Shelbyville | IN | First Merchants Bank, National Association | 10-Feb-12 |
| Charter National Bank and Trust | Hoffman Estates | IL | Barrington Bank & Trust Company, National Association | 10-Feb-12 |
| BankEast | Knoxville | TN | U.S. Bank, N.A. | 27-Jan-12 |
| Patriot Bank Minnesota | Forest Lake | MN | First Resource Bank | 27-Jan-12 |
| Tennessee Commerce Bank | Franklin | TN | Republic Bank & Trust Company | 27-Jan-12 |
| First Guaranty Bank and Trust Company of Jacksonville | Jacksonville | FL | CenterState Bank of Florida, N.A. | 27-Jan-12 |
| American Eagle Savings Bank | Boothwyn | PA | Capital Bank, N.A. | 20-Jan-12 |
| The First State Bank | Stockbridge | GA | Hamilton State Bank | 20-Jan-12 |
| Central Florida State Bank | Belleview | FL | CenterState Bank of Florida, N.A. | 20-Jan-12 |
| Western National Bank | Phoenix | AZ | Washington Federal | 16-Dec-11 |
| Premier Community Bank of the Emerald Coast | Crestview | FL | Summit Bank | 16-Dec-11 |
| Central Progressive Bank | Lacombe | LA | First NBC Bank | 18-Nov-11 |
| Polk County Bank | Johnston | IA | Grinnell State Bank | 18-Nov-11 |
| Community Bank of Rockmart | Rockmart | GA | Century Bank of Georgia | 10-Nov-11 |
| SunFirst Bank | Saint George | UT | Cache Valley Bank | 04-Nov-11 |
| Mid City Bank, Inc. | Omaha | NE | Premier Bank | 04-Nov-11 |
| All American Bank | Des Plaines | IL | International Bank of Chicago | 28-Oct-11 |
| Community Banks of Colorado | Greenwood Village | CO | Bank Midwest, N.A. | 21-Oct-11 |
| Community Capital Bank | Jonesboro | GA | State Bank and Trust Company | 21-Oct-11 |
| Decatur First Bank | Decatur | GA | Fidelity Bank | 21-Oct-11 |
| Old Harbor Bank | Clearwater | FL | 1st United Bank | 21-Oct-11 |
| Country Bank | Aledo | IL | Blackhawk Bank & Trust | 14-Oct-11 |
| First State Bank | Cranford | NJ | Northfield Bank | 14-Oct-11 |
| Blue Ridge Savings Bank, Inc. | Asheville | NC | Bank of North Carolina | 14-Oct-11 |
| Piedmont Community Bank | Gray | GA | State Bank and Trust Company | 14-Oct-11 |
| Sun Security Bank | Ellington | MO | Great Southern Bank | 07-Oct-11 |
| The RiverBank | Wyoming | MN | Central Bank | 07-Oct-11 |
| First International Bank | Plano | TX | American First National Bank | 30-Sep-11 |
| Citizens Bank of Northern California | Nevada City | CA | Tri Counties Bank | 23-Sep-11 |
| Bank of the Commonwealth | Norfolk | VA | Southern Bank and Trust Company | 23-Sep-11 |
| The First National Bank of Florida | Milton | FL | CharterBank | 09-Sep-11 |
| CreekSide Bank | Woodstock | GA | Georgia Commerce Bank | 02-Sep-11 |
| Patriot Bank of Georgia | Cumming | GA | Georgia Commerce Bank | 02-Sep-11 |
| First Choice Bank | Geneva | IL | Inland Bank & Trust | 19-Aug-11 |
| First Southern National Bank | Statesboro | GA | Heritage Bank of the South | 19-Aug-11 |
| Lydian Private Bank | Palm Beach | FL | Sabadell United Bank, N.A. | 19-Aug-11 |
| Public Savings Bank | Huntingdon Valley | PA | Capital Bank, N.A. | 18-Aug-11 |
| The First National Bank of Olathe | Olathe | KS | Enterprise Bank & Trust | 12-Aug-11 |
| Bank of Whitman | Colfax | WA | Columbia State Bank | 05-Aug-11 |
| Bank of Shorewood | Shorewood | IL | Heartland Bank and Trust Company | 05-Aug-11 |
| Integra Bank National Association | Evansville | IN | Old National Bank | 29-Jul-11 |
| BankMeridian, N.A. | Columbia | SC | SCBT National Association | 29-Jul-11 |
| Virginia Business Bank | Richmond | VA | Xenith Bank | 29-Jul-11 |
| Bank of Choice | Greeley | CO | Bank Midwest, N.A. | 22-Jul-11 |
| LandMark Bank of Florida | Sarasota | FL | American Momentum Bank | 22-Jul-11 |
| Southshore Community Bank | Apollo Beach | FL | American Momentum Bank | 22-Jul-11 |
| Summit Bank | Prescott | AZ | The Foothills Bank | 15-Jul-11 |
| First Peoples Bank | Port St. Lucie | FL | Premier American Bank, N.A. | 15-Jul-11 |
| High Trust Bank | Stockbridge | GA | Ameris Bank | 15-Jul-11 |
| One Georgia Bank | Atlanta | GA | Ameris Bank | 15-Jul-11 |
| Signature Bank | Windsor | CO | Points West Community Bank | 08-Jul-11 |
| Colorado Capital Bank | Castle Rock | CO | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | 08-Jul-11 |
| First Chicago Bank & Trust | Chicago | IL | Northbrook Bank & Trust Company | 08-Jul-11 |
| Mountain Heritage Bank | Clayton | GA | First American Bank and Trust Company | 24-Jun-11 |
| First Commercial Bank of Tampa Bay | Tampa | FL | Stonegate Bank | 17-Jun-11 |
| McIntosh State Bank | Jackson | GA | Hamilton State Bank | 17-Jun-11 |
| Atlantic Bank and Trust | Charleston | SC | First Citizens Bank and Trust Company, Inc. | 03-Jun-11 |
| First Heritage Bank | Snohomish | WA | Columbia State Bank | 27-May-11 |
| Summit Bank | Burlington | WA | Columbia State Bank | 20-May-11 |
| First Georgia Banking Company | Franklin | GA | CertusBank, National Association | 20-May-11 |
| Atlantic Southern Bank | Macon | GA | CertusBank, National Association | 20-May-11 |
| Coastal Bank | Cocoa Beach | FL | Florida Community Bank, a division of Premier American Bank, N.A. | 06-May-11 |
| Community Central Bank | Mount Clemens | MI | Talmer Bank & Trust | 29-Apr-11 |
| The Park Avenue Bank | Valdosta | GA | Bank of the Ozarks | 29-Apr-11 |
| First Choice Community Bank | Dallas | GA | Bank of the Ozarks | 29-Apr-11 |
| Cortez Community Bank | Brooksville | FL | Florida Community Bank, a division of Premier American Bank, N.A. | 29-Apr-11 |
| First National Bank of Central Florida | Winter Park | FL | Florida Community Bank, a division of Premier American Bank, N.A. | 29-Apr-11 |
| Heritage Banking Group | Carthage | MS | Trustmark National Bank | 15-Apr-11 |
| Rosemount National Bank | Rosemount | MN | Central Bank | 15-Apr-11 |
| Superior Bank | Birmingham | AL | Superior Bank, National Association | 15-Apr-11 |
| Nexity Bank | Birmingham | AL | AloStar Bank of Commerce | 15-Apr-11 |
| New Horizons Bank | East Ellijay | GA | Citizens South Bank | 15-Apr-11 |
| Bartow County Bank | Cartersville | GA | Hamilton State Bank | 15-Apr-11 |
| Nevada Commerce Bank | Las Vegas | NV | City National Bank | 08-Apr-11 |
| Western Springs National Bank and Trust | Western Springs | IL | Heartland Bank and Trust Company | 08-Apr-11 |
| The Bank of Commerce | Wood Dale | IL | Advantage National Bank Group | 25-Mar-11 |
| Legacy Bank | Milwaukee | WI | Seaway Bank and Trust Company | 11-Mar-11 |
| First National Bank of Davis | Davis | OK | The Pauls Valley National Bank | 11-Mar-11 |
| Valley Community Bank | St. Charles | IL | First State Bank | 25-Feb-11 |
| San Luis Trust Bank, FSB | San Luis Obispo | CA | First California Bank | 18-Feb-11 |
| Charter Oak Bank | Napa | CA | Bank of Marin | 18-Feb-11 |
| Citizens Bank of Effingham | Springfield | GA | Heritage Bank of the South | 18-Feb-11 |
| Habersham Bank | Clarkesville | GA | SCBT National Association | 18-Feb-11 |
| Canyon National Bank | Palm Springs | CA | Pacific Premier Bank | 11-Feb-11 |
| Badger State Bank | Cassville | WI | Royal Bank | 11-Feb-11 |
| Peoples State Bank | Hamtramck | MI | First Michigan Bank | 11-Feb-11 |
| Sunshine State Community Bank | Port Orange | FL | Premier American Bank, N.A. | 11-Feb-11 |
| Community First Bank Chicago | Chicago | IL | Northbrook Bank & Trust Company | 04-Feb-11 |
| North Georgia Bank | Watkinsville | GA | BankSouth | 04-Feb-11 |
| American Trust Bank | Roswell | GA | Renasant Bank | 04-Feb-11 |
| First Community Bank | Taos | NM | U.S. Bank, N.A. | 28-Jan-11 |
| FirsTier Bank | Louisville | CO | No Acquirer | 28-Jan-11 |
| Evergreen State Bank | Stoughton | WI | McFarland State Bank | 28-Jan-11 |
| The First State Bank | Camargo | OK | Bank 7 | 28-Jan-11 |
| United Western Bank | Denver | CO | First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company | 21-Jan-11 |
| The Bank of Asheville | Asheville | NC | First Bank | 21-Jan-11 |
| CommunitySouth Bank & Trust | Easley | SC | CertusBank, National Association | 21-Jan-11 |
| Enterprise Banking Company | McDonough | GA | No Acquirer | 21-Jan-11 |
| Oglethorpe Bank | Brunswick | GA | Bank of the Ozarks | 14-Jan-11 |
| Legacy Bank | Scottsdale | AZ | Enterprise Bank & Trust | 07-Jan-11 |
| First Commercial Bank of Florida | Orlando | FL | First Southern Bank | 07-Jan-11 |
Sources:
- https://www.fdic.gov/resources/resolutions/bank-failures/failed-bank-list/
- https://www.fdic.gov/news/press-releases/2023/pr23015.html
- https://www.fdic.gov/news/press-releases/2023/pr23034.html