The Federal Reserve's recent signals are making it clearer than ever: a December 2025 interest rate cut is looking less and less likely. While the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) did reduce the federal funds rate by 25 basis points in October 2025, the freshly released minutes from their November 19 meeting reveal a palpable hesitation among policymakers about cutting rates again in December.
Fed Signals Growing Reluctance to Interest Rate Cut in December 2025
This caution stems from a difficult balancing act between wanting to support employment and the persistent need to bring inflation fully back down to their 2% target. As things stand now, the path forward for interest rates is far from certain, and a pause in December seems to be the leading scenario.
For months, the big question on everyone's mind has been: when will the Fed start lowering interest rates? After a series of hikes to combat soaring inflation, the economy has shown signs of cooling, leading many to anticipate rate cuts. Yet, the latest insights from the Fed suggest that while they've eased policy a bit, they're not quite ready to keep pushing rates down. This is a critical moment, and understanding why the Fed is hesitant is key to grasping what might happen next in our economy, from borrowing costs to job markets.
The October Meeting: A Step Back, Not a Leap Forward
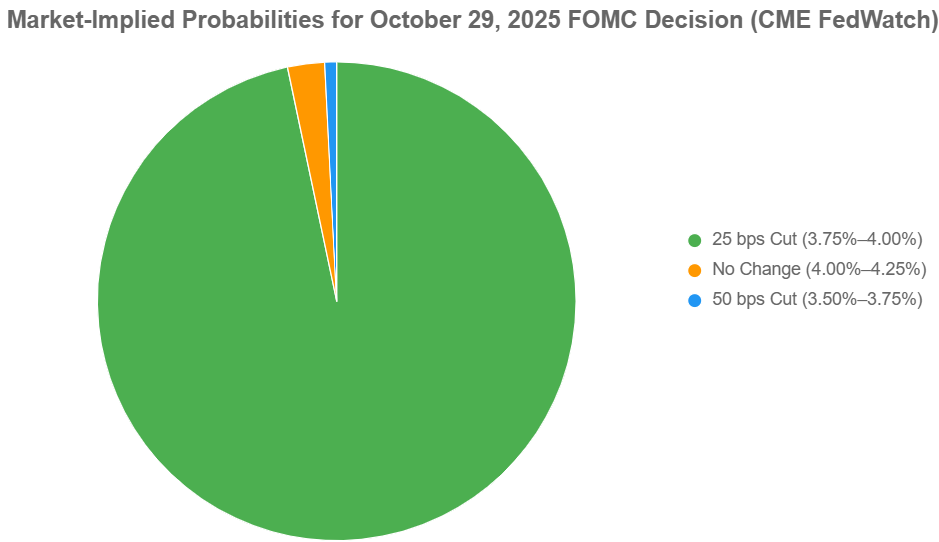
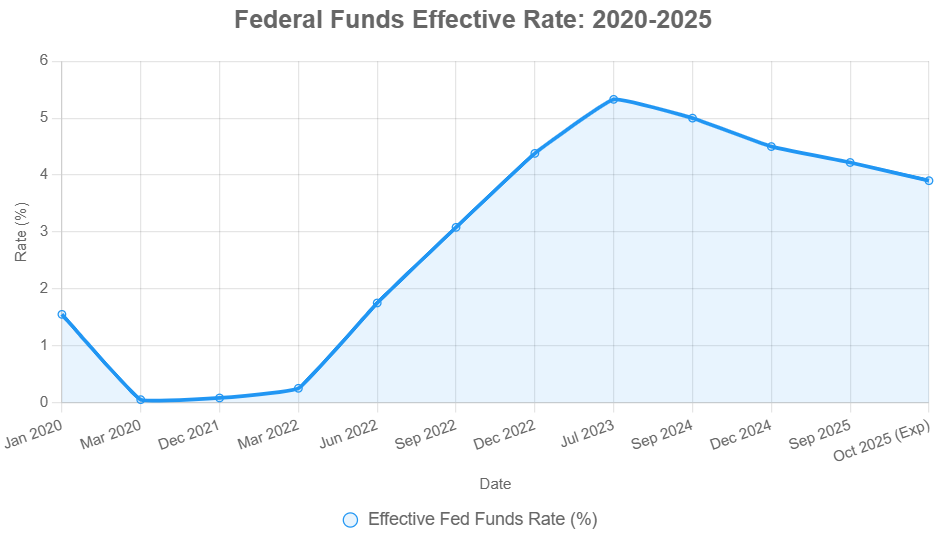
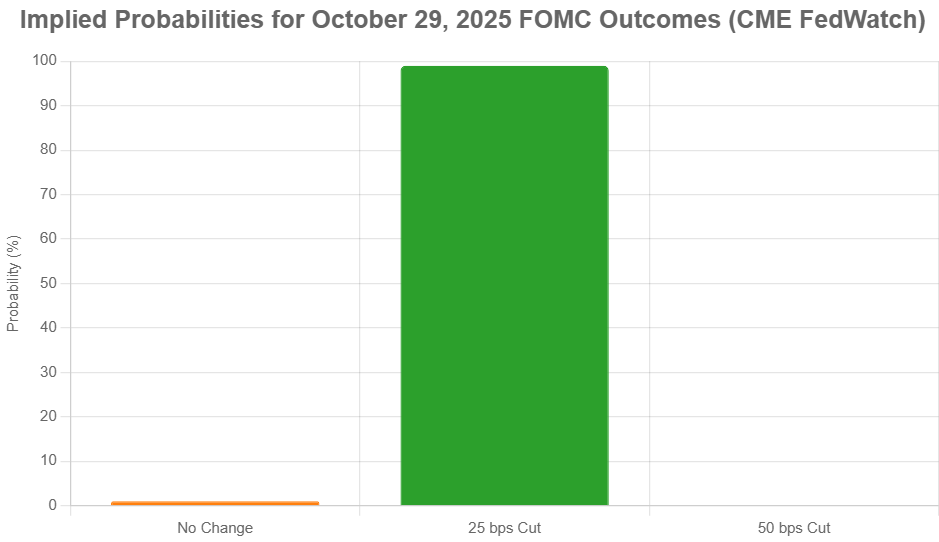
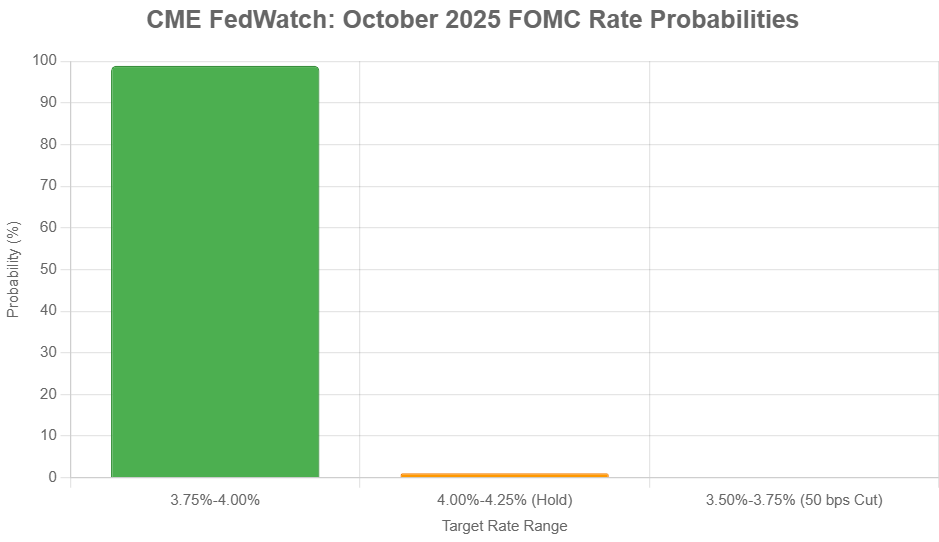
The meeting on October 28–29, 2025, resulted in the Fed's second rate cut of the year, bringing the target federal funds rate down to a range of 3.75%–4.00%. This move was intended to help bolster employment as economic growth showed signs of slowing. However, the vote was closer than expected, with a 10–2 split.
This wasn't just a minor disagreement; it highlighted genuinely different views within the committee. One policymaker voted for a more substantial 50 basis point cut, believing it was needed to more aggressively tackle rising unemployment risks. On the other hand, another dissenter felt it was better to hold rates steady, emphasizing the need for more solid proof that inflation was truly under control.
In my opinion, this split vote is a significant clue. It tells us that even when the Fed does decide to ease, there are substantial concerns about doing too much, too soon. The Fed's main goal is to achieve both maximum employment and price stability (keeping inflation at 2%). Right now, these goals seem to be pulling in slightly different directions, making their decisions incredibly complex.
Additionally, the Fed also announced it would end its balance sheet runoff by December 1, 2025. This is essentially a way to inject more liquidity into the financial system. It’s like them saying, “We're easing on one front with rates, but we're also preparing to ease liquidity, giving us more flexibility for future decisions.” They are trying to carefully manage the system without creating new problems.
Digging into the Minutes: What Policymakers Are Really Thinking
The minutes from the November 19 release are where we get the real meat of the discussion. They revealed that many FOMC participants expressed reservations about cutting rates again in December. Why? The minutes pointed to a couple of main reasons:
- Inflation is Still Sticky: While inflation has come down considerably from its peaks, it's currently hovering around 2.8% (for core PCE), which is still above the Fed's 2% target. Some policymakers worried that further rate cuts could risk inflation becoming entrenched, meaning it gets stuck at a higher level than desired. They specifically noted that “further policy rate reductions could add to the risk of higher inflation becoming entrenched or could be misinterpreted as implying a lack of policymaker commitment to the 2 percent inflation objective.” That's a direct quote from the minutes, folks, and it’s pretty telling.
- Uncertainty from Economic Data: The recent U.S. government shutdown caused disruptions in data collection, making it harder for the Fed to get a clear picture of the economy's true health. This lack of solid, up-to-date information makes making big policy decisions, like cutting rates, a much riskier proposition.
Key Concerns Highlighted in the Minutes:
- Inflation Risks: Upside risks to inflation were described as “elevated.”
- Data Gaps: The government shutdown led to a high degree of uncertainty about the economic outlook.
- Policy Commitment: A desire to signal unwavering commitment to the 2% inflation goal.
The minutes suggest that while the overall economy is still expanding at a “moderate pace,” fueled by consumer spending and exports, these underlying concerns about prices are weighing heavily on the minds of Fed officials.
The Employment Picture: Cooling, But Not Collapsing
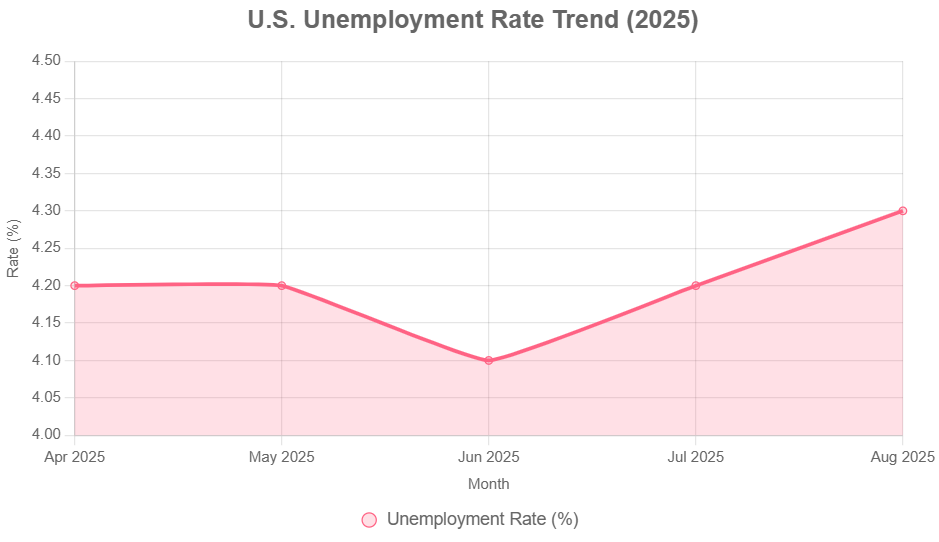
On the flip side, the labor market has shown clear signs of cooling. Job gains have slowed, and the unemployment rate has edged up slightly, now around 4.2%. This is still historically low, and layoff rates remain subdued. The Fed acknowledges this softening and sees it as one of the main reasons for the October rate cut. However, the minutes also indicate that this employment picture, while weakening, isn't yet dire enough to override the inflation concerns for many.
The Fed's dual mandate is crucial here: they need to keep prices stable and support maximum employment. When inflation is stubbornly above target, and the job market is cooling but not alarming, the tendency is to prioritize getting inflation back to 2% before aggressively cutting rates to boost jobs. This is a delicate dance, and right now, inflation seems to be the heavier foot.
December Rate Cut Scenarios: What's Likely and Why
Based on the minutes and recent market reactions, here's how I see the potential scenarios for the December 16–17 FOMC meeting:
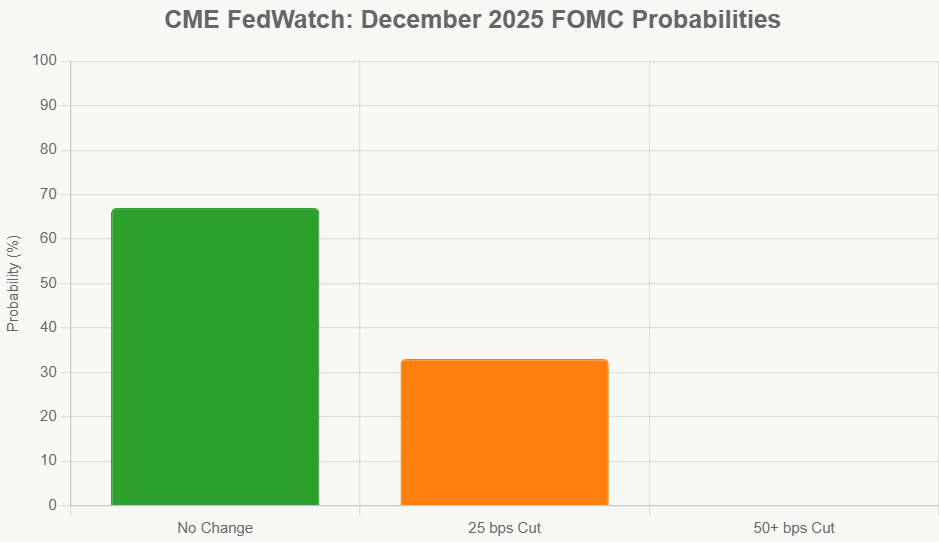
1. The Hawkish Hold (Most Probable)
- What it means: The Fed keeps interest rates unchanged at the current 3.75%–4.00% range.
- Why it's likely: This scenario aligns with the growing reluctance expressed in the minutes. If incoming data in November (like jobs reports and inflation figures) shows continued evidence of inflation staying above target or a strong labor market, the Fed will likely hold. This sends a signal that they need more convincing evidence that inflation is on a sustainable path back to 2%.
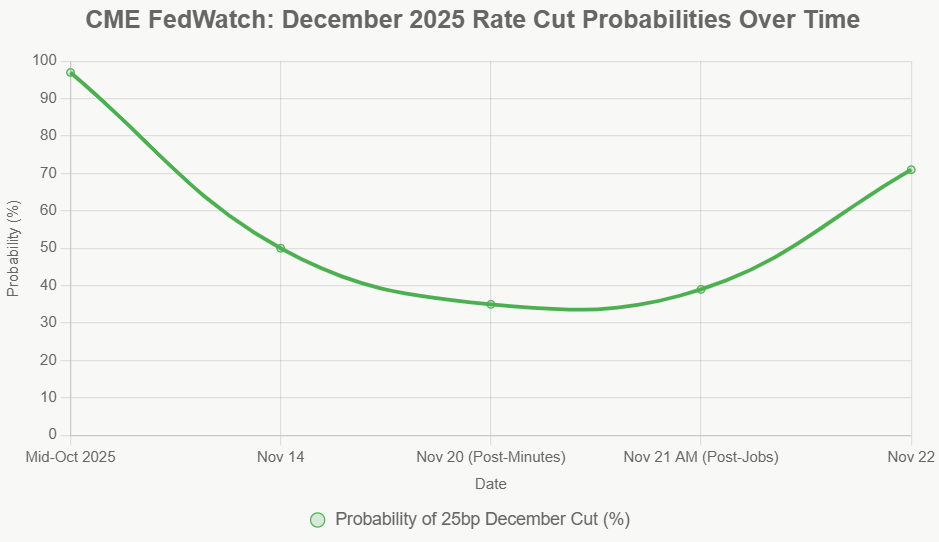
- Market Implication: This would likely temper expectations for rapid rate cuts in early 2026, potentially leading to slightly higher bond yields and a steadier stock market. As of my last check, market odds favored this outcome at around 67%.
2. The Dovish Cut (Still Possible, but Less Likely Now)
- What it means: The Fed cuts rates by 25 basis points, bringing the target range down to 3.50%–3.75%.
- Why it could happen: This would align more closely with the September “dot plot” projections, which suggested two rate cuts by year-end 2025. If November's jobs report shows a significant weakening (e.g., fewer than 150,000 new jobs) or inflation data unexpectedly cools sharply, the Fed might opt for a cut to support employment.
- Market Implication: A cut would likely boost stock markets and lower borrowing costs, but it could also reignite fears of inflation returning. This scenario's probability, which had briefly surged earlier in the week, has now fallen to around 33%.
3. Aggressive Easing (Very Unlikely)
- What it means: A cut of 50 basis points or more.
- Why it's unlikely: This would require a truly alarming economic shock, like a rapid surge in unemployment or a sudden deflationary scare, neither of which appears imminent based on current data. This scenario would echo the more aggressive dissent seen in the October meeting but doesn't fit the Fed's current measured approach.
Looking Beyond December: The 2026 Outlook
The September 2025 “dot plot” (which is the Fed's projection of where it sees interest rates going) is still a key reference point. It indicated a median federal funds rate of 3.4% by the end of 2025, implying one more cut from the current level. For 2026, the projection was for rates to move lower, toward a neutral rate of around 3%. While the October minutes introduce ambiguity about December, the longer-term trend still points toward eventual easing. However, how quickly and how smoothly that easing occurs is the big question.
Historical Context: A Turnaround in Progress
It's helpful to remember where we've come from. After aggressively hiking rates from near zero in 2022 to combat runaway inflation, the Fed began its pivot to easing in late 2024.
| Event | Change (bps) | Target Range (%) |
|---|---|---|
| July 2023 (Peak) | +25 | 5.25–5.50 |
| Sep 2024 | -50 | 4.75–5.00 |
| Nov 2024 | -25 | 4.50–4.75 |
| Dec 2024 | -25 | 4.25–4.50 |
| Sep 2025 | -25 | 4.00–4.25 |
| Oct 2025 | -25 | 3.75–4.00 |
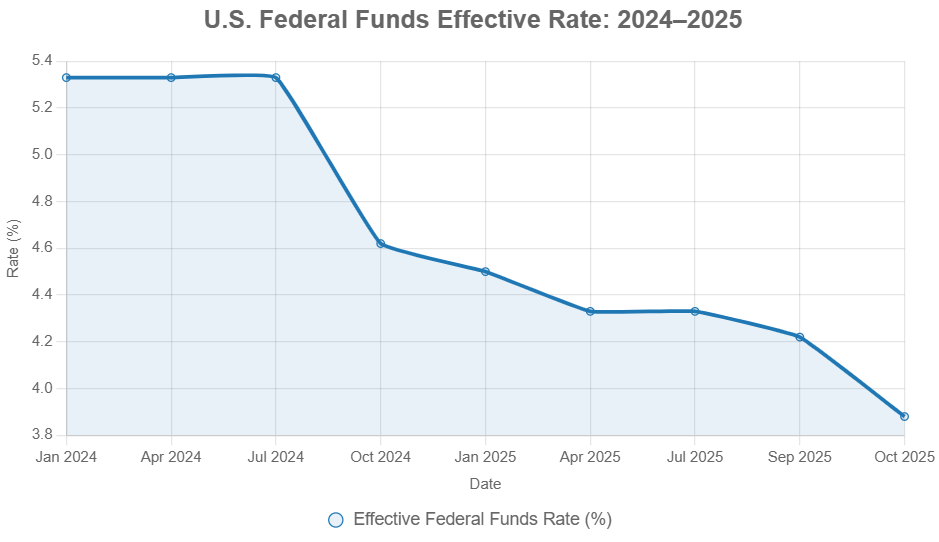
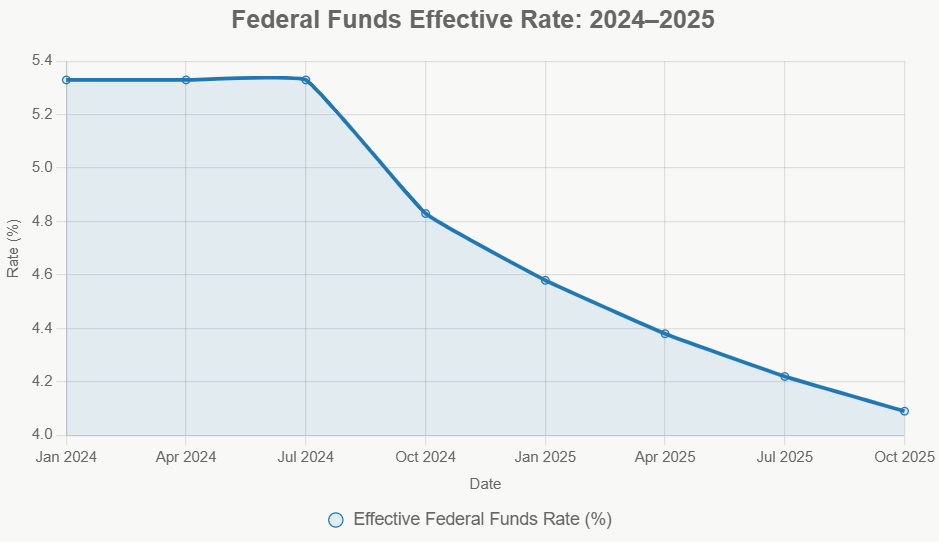
This table shows a cumulative easing of 150 basis points since September 2024. The effective federal funds rate has followed a similar downward trend, currently sitting around the 4.09% mark for October 2025. This easing cycle is happening as inflation has calmed but not yet fully settled at the 2% target.
Implications for You: What This Means for Your Wallet
So, what does this growing Fed reluctance mean for everyday people and investors?
- For Borrowers: If the Fed pauses in December, it means that borrowing costs might not fall as quickly as some had hoped. Mortgage rates, currently around 6.5%, might stabilize or even tick up slightly if inflation fears resurface. Auto loans (around 7%) and credit card rates (around 20%) won't see any immediate relief from further Fed cuts in December.
- For Savers: This is good news for savers. If rates stay higher for longer, you'll continue to earn decent interest on your savings accounts, CDs, and money market funds, which are currently offering yields around 4%.
- For Investors: A December pause might temper the immediate optimism for a strong market rally driven by easy money. However, it could also reinforce the narrative of a “soft landing”—an economy that cools without plunging into recession. Investors will be watching closely for any signs of economic distress that might force the Fed's hand later. Strong November jobs data, for example, could be seen as positive for the economy but negative for immediate rate cut hopes.
- For Businesses: Businesses will likely face continued higher borrowing costs, which could influence investment decisions. However, stable inflation expectations might provide some predictability. The end of QT could also provide some liquidity benefits.
My Take: A Measured Approach is Likely
From my perspective, the Fed is in a tough spot, and their caution is warranted. The economy has been surprisingly resilient, but the battle against inflation isn't completely won. The minutes from the October meeting strongly suggest that the Committee wants to be very sure before embarking on another round of rate cuts.
I believe the most likely scenario is a hawkish hold in December. This allows the Fed to gather more data, assess the impact of the October cut, and see if inflation truly continues on its downward path. They've learned from history that prematurely cutting rates when inflation is still a concern can be a costly mistake, potentially leading to the inflationary spirals of the 1970s.
However, I also believe they are keenly aware of employment risks. If the job market shows signs of significant weakness in the coming weeks, they won't hesitate to cut rates to fulfill their mandate. The key takeaway is that the Fed is truly data-dependent, and their decisions will be guided by the incoming economic reports.
The Fed's signals of growing reluctance to cut interest rates in December 2025 reflect a delicate balancing act against persistent inflation. Explore the FOMC minutes, economic backdrop, and expert outlooks to understand the evolving monetary policy outlook.
Invest in Real Estate While Rates Are Dropping — Build Wealth
If the Federal Reserve moves forward with another rate cut in December, investors could gain a valuable window to secure more favorable financing terms and scale their portfolios ahead of renewed buyer demand.
Lower borrowing costs would boost cash flow and enhance overall returns, especially for those positioned to act quickly
Work with Norada Real Estate to find turnkey, income-generating properties in stable markets—so you can capitalize on this easing cycle and grow your wealth confidently.
NEW TURNKEY DEALS JUST ADDED!
Talk to a Norada investment counselor today (No Obligation):
(800) 611-3060
Want to Know More?
Explore these related articles for even more insights:
- Fed Cuts Interest Rate Today for the Second Time in 2025
- Fed Interest Rate Decision Today: Markets Prepare for Quarter-Point Rate Cut
- Fed Interest Rate Forecast Q4 2025: Target Range Could Hit 3.50%–3.75%
- Fed Interest Rate Forecast for the Next 12 Months
- Federal Reserve Cuts Interest Rate by 0.25%: Two More Cuts Expected in 2025
- Interest Rate Predictions for the Next 3 Years: 2025, 2026, 2027
- When is Fed's Next Meeting on Interest Rate Decision in 2025?
- Interest Rate Predictions for the Next 10 Years: 2025-2035
- Interest Rate Predictions for 2025 by JP Morgan Strategists
- Interest Rate Predictions for Next 2 Years: Expert Forecast
- Market Reactions: How Investors Should Prepare for Interest Rate Cut
- Impact of Interest Rate Cut on Mortgages, Car Loans, and Your Wallet