Keeping a pulse on new home construction is crucial for investors like us. It's a window into what kind of housing stock will be available down the road, potentially impacting everything from rental rates to resale values. So, let's unpack the latest data for 2024 and see what insights we can glean.
Housing Starts refer to the number of new residential construction projects that have begun during any particular month. Estimates of housing starts include units in structures being rebuilt on an existing foundation.
Building permits, on the other hand, are issued by local governments to allow builders to begin the construction of a new home or to make significant renovations to an existing home. Building permits are usually required for any new construction or remodeling that involves changes to the structural or mechanical systems of a home.
Housing construction refers to the actual building of the residential structure, which includes everything from laying the foundation to framing the walls, installing electrical and plumbing systems, and finishing the interior and exterior of the building.
The sequence of new housing construction events typically goes as follows:
A builder obtains a building permit from the local government, which allows them to start construction on a new housing unit.
Once construction begins, it is counted as a housing start. The construction process continues until the housing unit is completed and ready for occupancy, at which point it is considered part of the housing stock.
So, building permits come first, followed by housing starts, and then housing construction. However, it is important to note that not all permits lead to starts and not all starts to lead to completed construction. Some permits may expire before construction begins, and some starts may be delayed or canceled due to various reasons such as changes in market conditions or financing issues.
New Residential Construction Trends – June 2024

Building Permits
According to recent data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, in June 2024, the seasonally adjusted annual rate of privately-owned housing units authorized by building permits reached a noteworthy 1,446,000. This figure represents a 3.4% increase over the revised rate of 1,399,000 recorded in May. However, it is worth noting that there is a year-over-year decline, as the rate was 3.1% lower than the 1,493,000 permits authorized in June 2023.
The data reveals a mixed trend within the single-family housing segment. Authorizations for single-family homes stood at 934,000, showing a 2.3% decline compared to May's revised figure of 956,000. In contrast, multi-family housing units (buildings with five units or more) showed resilience, with authorizations reaching 460,000 in June.
Key Insights:
- Regulatory Environment: The increase in building permits may signal a loosening of regulations or an active approach by developers to secure approvals before potential changes in the regulatory landscape.
- Market Demand: The decline in single-family authorizations may reflect a shift in buyer preferences, economic uncertainties, or higher interest rates affecting individual homebuyers more acutely than large-scale developments.
Housing Starts
When it comes to housing starts, June's seasonally adjusted annual rate was 1,353,000. This marks a 3.0% increase from the revised estimate of 1,314,000 in May but reflects a 4.4% decrease from the June 2023 rate of 1,415,000.
For single-family housing starts, the numbers continued to show a downward trend, with a rate of 980,000 in June, down 2.2% from May's revised figure of 1,002,000. Meanwhile, multi-family housing starts have exhibited slight variability, with units in buildings of five or more dropping to 360,000.
Key Insights:
- Economic Factors: The reduced starts in both single-family and multi-family homes compared to the previous year may point to challenges such as higher material costs, labor shortages, and shifting buyer sentiment amidst a fluctuating economy.
- Urban vs. Suburban Trends: Builders are increasingly focusing on urban locations, aligning with demographic trends favoring city living, although suburban areas remain popular due to space and affordability considerations.
Housing Completions
On a positive note, privately-owned housing completions surged in June, reaching a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1,710,000, which is a solid 10.1% increase over the revised May estimate of 1,553,000 and a 15.5% increase compared to the 1,480,000 completions recorded in June 2023.
The breakdown of completions shows that single-family home completions stood at 1,037,000, slightly up by 1.8% from May's figures. Furthermore, multi-family completions reflected robust activity at 656,000, indicating a continued demand for rental properties and multi-family units.
Key Insights:
- Supply Chain Resolution: The rise in housing completions suggests improvements in supply chain efficiencies and the construction process, allowing builders to better navigate previous delays.
- Rental Market Demand: The continued strength in multi-family completions indicates a persistent demand for rental housing, which can be attributed to economic factors that may make home purchasing less accessible for some demographics.
The data from June 2024 presents a complex picture of the residential construction landscape. While the uptick in building permits and housing completions suggests a responsive market, the struggles in single-family authorizations and housing starts imply underlying challenges that could influence future construction trends.
New-Home Construction Forecast for 2024
As the real estate landscape continues to evolve, the forecast for new-home construction in 2024 is brimming with optimism. Home buyers, frustrated by the scarcity of existing inventory, are turning to builders for solutions. The data reveals a surge in construction activities, with builders employing innovative sales incentives to attract house hunters.
The Rise of New-Home Market
The new-home market is emerging as a dominant player, set to shape the real estate landscape in 2024. According to Ali Wolf, Chief Economist at housing research firm Zonda, the trend is expected to continue gaining momentum. Speaking at the International Builders' Show in Las Vegas, Wolf emphasized the increasing role of new-home sales, which traditionally constituted 10% to 12% of the market for single-family homes but now account for over 30%.
Addressing Affordability Concerns
With existing-home prices soaring to record highs, home builders are proactively addressing buyers' affordability concerns. The shortage of existing homes for sale has created an opportunity for new-home construction to cater to a broader audience. Danielle Hale, Chief Economist at realtor.com®, notes that 40% of home buyers consider buying new homes to “avoid renovations or problems,” highlighting the appeal of turnkey solutions.
Buyers' Motivations and Incentives
Zonda's research indicates that 40% of home buyers opt for new homes to avoid the hassles of renovations, while 25% are driven by the scarcity of existing inventory. Additionally, 25% appreciate the ability to choose and customize their home's design. In response to these preferences, builders are introducing enticing sales incentives.
The most popular incentive, according to Wolf, has been mortgage buydowns. To ease buyers' fears and boost confidence in the market, builders are offering financial incentives such as funds towards closing costs, with some reaching up to $20,000. Moreover, “flex dollars” are becoming a sought-after perk, allowing buyers to invest in home upgrades according to their preferences.
New-Home Construction Outlook for 2024
The momentum in new-home construction is poised to shape the real estate landscape throughout 2024. As buyers seek alternatives to the challenges posed by existing inventory, builders are stepping up their efforts to provide turnkey solutions and attractive incentives. The forecast indicates a positive trajectory for the new-home market, with affordability and customization driving the preferences of home buyers.
Builders' Positive Outlook and Challenges Ahead
Builders are approaching 2024 with a bullish outlook, fueled by a forecast that anticipates a 4.7% increase in single-family housing starts nationwide this year. The momentum is expected to continue into 2025, with an additional 4.2% growth, reaching an impressive pace of 1.3 million units, as reported by the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB).
Meeting the Housing Deficit Challenge
However, economists are urging builders to do more to address the nation's housing deficit. According to Robert Dietz, Chief Economist of NAHB, building over 1.15 million single-family homes annually is crucial to reducing the housing deficit. Despite the ambitious goal, builders are facing formidable challenges that hinder their capacity to build at the required pace.
Obstacles in the Path of Builders
Builders are grappling with multiple challenges, including higher prices, shortages of lumber, lots, and labor. These factors are stifling their ability to meet the growing demand for new homes. Dietz highlighted the impact of rising regulatory costs, which account for nearly 24% of the final sales price—or a significant $93,870—for a new single-family home. This underscores the complexity and cost implications of complying with building codes and zoning regulations.
Optimism Despite Challenges
Despite these headwinds, builders remain remarkably optimistic, buoyed by the surge in consumer demand. According to Ali Wolf, Chief Economist at Zonda, 80% of builders anticipate initiating more home starts in the current year. Furthermore, a substantial 51% of builders expect starts to increase by more than 10% compared to the previous year, showcasing a strong belief in the resilience of the market.
The Path Forward: Strategies for Success
As builders navigate the challenges posed by higher prices, material shortages, and regulatory hurdles, strategic planning becomes imperative. Finding innovative solutions to streamline the construction process, exploring alternative materials, and advocating for regulatory reforms are essential components of overcoming these obstacles. The commitment to meeting the nation's housing deficit while ensuring affordability remains a shared goal among builders.
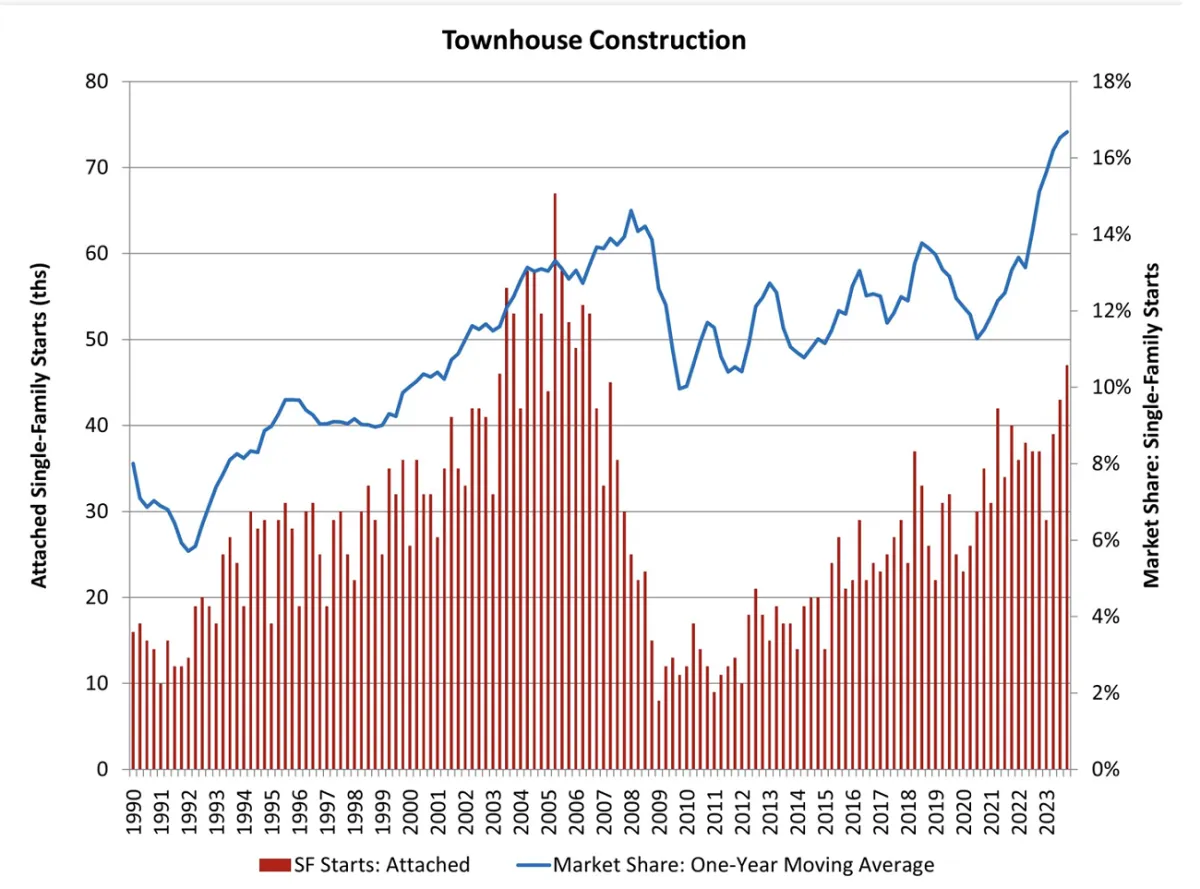
The Townhouse Boom: A Shift in Housing Trends
As builders adapt to the challenges of affordability and lot shortages, the real estate landscape is witnessing a notable shift with the rise of townhome construction. Townhouses have experienced a surge, reaching their highest rate in over 17 years, according to an analysis of Census data by the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB).
Responding to Affordability and Lot Woes
Builders are diversifying their product offerings to address affordability concerns and lot shortages. Townhome construction, characterized by single-family attached housing, has become an attractive option for both builders and home buyers. This housing style often comes with a lower price tag, making it a viable solution in the current real estate landscape.
Impressive Growth in Townhouse Starts
The fourth quarter of 2023 saw a remarkable 27% increase in single-family attached starts compared to the same period in 2022. Townhouses, overall, accounted for nearly 20% of the total housing starts in the final quarter of 2023. This surge signifies a growing preference for townhomes among home buyers, offering a more affordable and accessible housing option.
Bright Spots in the New-Home Sector
Robert Dietz, Chief Economist of NAHB, identifies townhouse markets as one of the bright spots in the new-home sector. He expresses optimism about this segment continuing to outperform, pointing to a shift in preferences among home buyers. Both young and old demographics are increasingly seeking medium-density residential neighborhoods, such as urban villages, that provide walkable environments and a range of amenities.
Meeting the Demand for Walkable Environments
The appeal of townhouses extends beyond affordability, with an increasing number of home buyers valuing walkable environments and communal amenities. Urban villages, characterized by medium-density residential developments, are gaining popularity as they offer a lifestyle that aligns with the preferences of modern home buyers.











